Posted on 22 Feb 2023
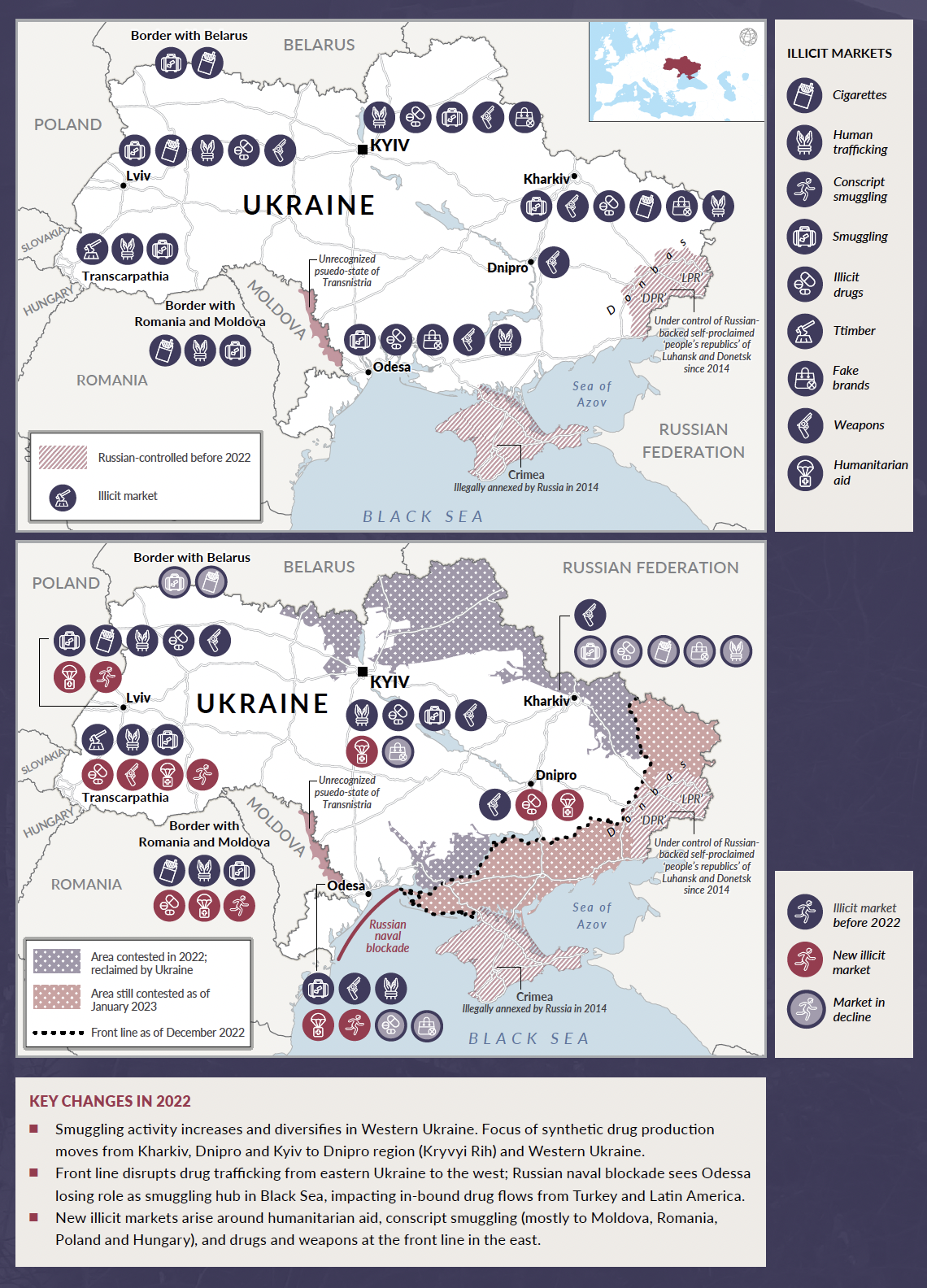
Before February 2022, Russian and Ukrainian organized crime formed the strongest criminal ecosystem in Europe. Having developed along similar lines in the 1990s, Russian and Ukrainian criminal groups and networks controlled a lucrative transnational smuggling highway between Russia and Western Europe that carried gold, timber, tobacco, coal, counterfeit/untaxed goods, humans and drugs. At the more politically connected end of the spectrum, corrupt officials and criminal bosses from both countries exploited Ukraine’s role as a transit country for Russian gas to siphon off millions of dollars, while Ukraine’s oligarch class exerted a strong grip over the country’s economic, political and information spheres.
Kyiv made serious efforts to tackle organized crime and corruption after the 2014 Maidan Revolution but results were mixed, especially in the case of judicial reform; meanwhile, the conflict in the Donbas region helped bolster an array of illicit economies and criminal actors. For organized crime, business was generally good.
The Russian invasion has inflicted a profound shock to this ecosystem. With the war, collaboration between Russian and Ukrainian organized crime interests became impossible due to the political situation (which led many criminals to break such ties) and the pragmatic challenge of smuggling across what was now a violently contested and dynamic front line. Many Ukrainian crime bosses chose to leave the country, as did many oligarchs, including several accused of pro-Russian sympathies. Martial law and the curfew also initially constrained criminal activity. According to senior sources in the Ukrainian police, incidents of armed robberies declined by a factor of between three and four, and the homicide rate dropped to almost zero at the beginning of the war (although this may partly reflect the impact of the war on reporting in the early days of the war). It may be that the impact of the invasion also whittled out some less robust and resilient organized crime groups: according to data from the general prosecutor’s office, the number of organized crime groups under investigation decreased from 499 in 2021 to 395 in 2022 (although this decline alternatively could reflect dimished investigative capacity).
This report explores the changing dynamics in the political economy of Ukrainian organized crime up till December 2022 and maps how the criminal landscape has adapted to the new situation. Given the complexity of the impact of the war in Ukraine on organized crime in both parties to the conflict, the GI-TOC is producing two reports. This report concentrates on developments within Ukraine’s internationally recognized borders – with the exception of the so-called Luhansk and Donetsk ‘people’s republics’ (LDNR) in the Donbas region, which broke away from Kyiv in 2014 with Russian backing and assistance, and Crimea, which Russia illegally annexed the same year. The impact of the conflict on organized crime in these areas and on Russian organized crime more generally will be discussed in a separate report, which will assess trends in sanctions busting and money laundering, changes in trafficking flows east of Ukraine and how Russian organized crime groups have responded to the conflict.