Posted on 28 May 2020
The flow of heroin from Asian production points to the coastal shores of eastern and southern Africa is not new. Whereas the first heroin transit routes in the region in the 1970s relied heavily on maritime transport to enter the continent, a number of transport modes and urban centres of the interior have increasingly become important features in the current movement of heroin in this region. Interior transit hubs and networks have developed around air transport nodes that use regular regional and international connections to ship heroin. As regional air routes proliferated and became more efficient, their utility and value for the heroin trade increased as well. Heroin is also consolidated and shipped over a frequently shifting network of overland routes, moving it deeper into the African interior in a south-westerly direction across the continent.
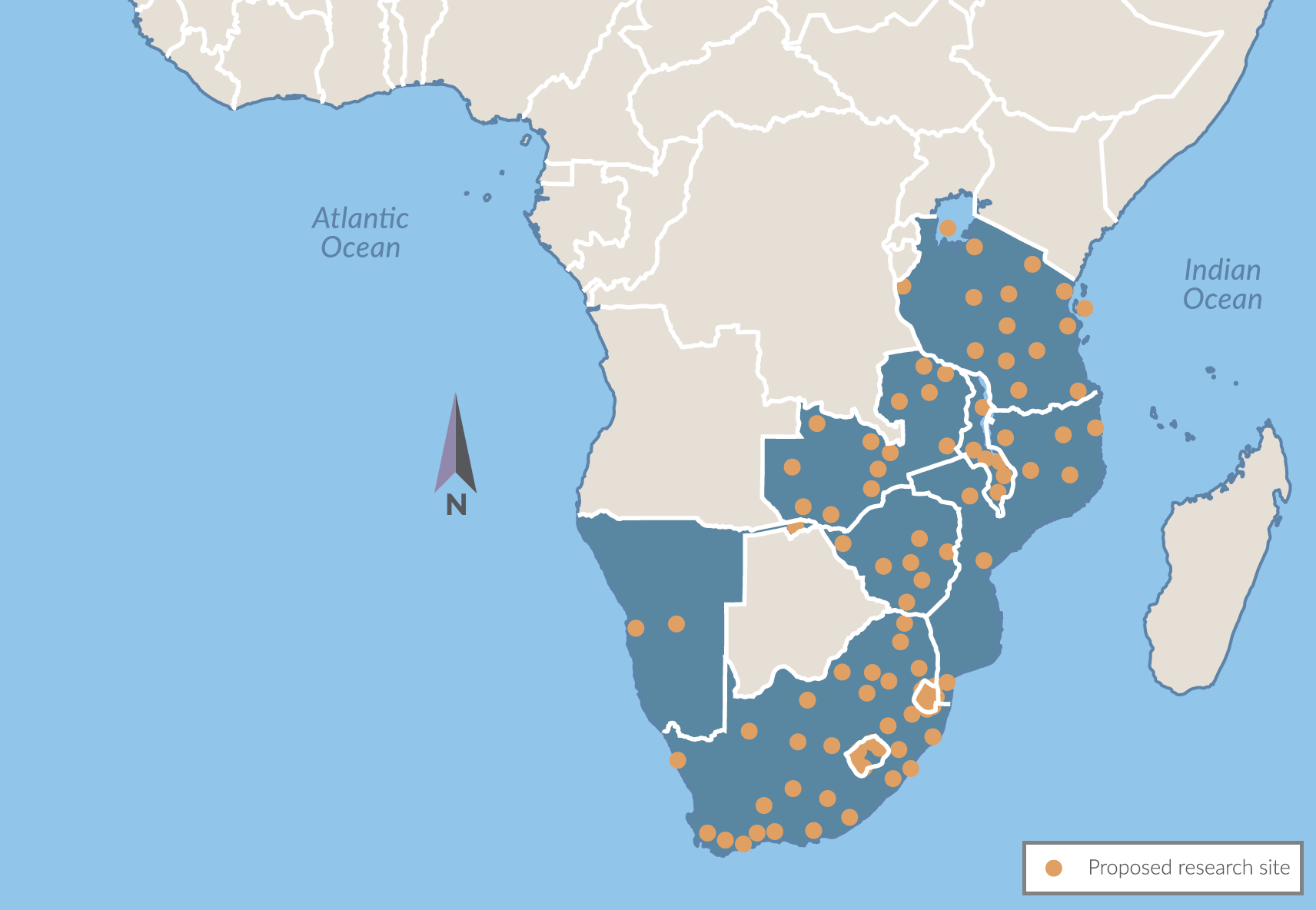
Consequently, a shallow flood of heroin has gradually seeped across the region, and this has had a significant impact on the many secondary towns found along the continent’s transcontinental road networks. These places, in turn, have spawned their own small local heroin markets, and become waypoints in rendering sustainable the now chronic, metered progression of heroin’s resolute geographic diffusion across the region.
The impact of this creeping spread of heroin on regional state development has been significant and, paradoxically, symbiotic. The emerging illicit African drug market environments may represent credible threats to the development and security of the region’s nascent independent state institutions and structures. At the same time, these markets have also presented new and considerable sources of economic livelihood and opportunity for the continent’s ever-expanding population of poor, disenfranchised and vulnerable people. A surrogate ‘drug working class’ has emerged as a socio-economic sequela to more traditional, yet increasingly limited, licit income opportunities.